5 June 2023

The annual rate of inflation as measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) rose 10.1% in March, a slightly slower pace than the 10.4% in February (1).
The sharp decline in wholesale energy prices seen in the last few months is starting to flow through into lower energy bills for businesses and households.
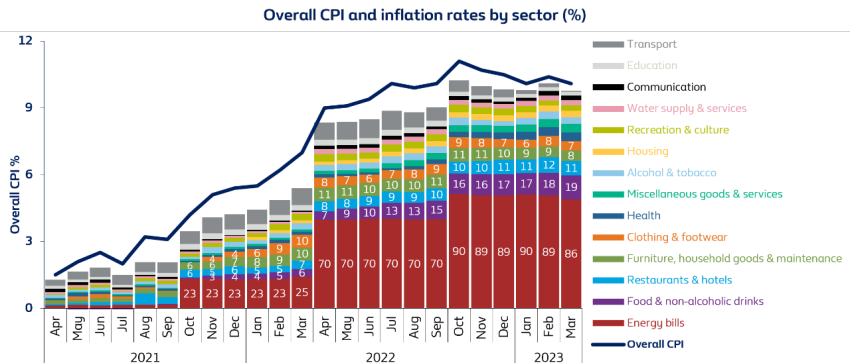
Inflation has been above the Bank of England’s 2% target since May 2021, despite the Bank raising interest rates 11 consecutive times to 4.25%.
The largest contributor to inflation is the cost of energy, which peaked in October 2022 when prices soared by 90%.
The cost of energy did not account for much of CPI prior to October 2021, but since then it has increased in leaps and bounds.
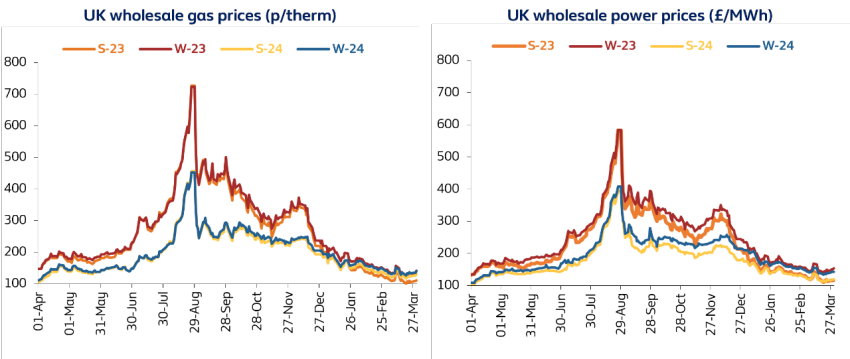
Inflation is expected to drop sharply later this year as gas and electricity prices in wholesale markets have fallen by as much as 85% and 80% respectively since their peak last August (2).
Season ahead (Summer 23) natural gas prices were trading around 110p per therm by the end of March 2023, having hit 726p per therm last August as Russia cut Europe’s gas supplies.
Meanwhile, power prices for Summer 23 were trading at £117/MWh, down from £583/MWh over the same period.
The key drivers behind falling wholesale energy prices include:
The views, opinions and positions expressed within the British Gas Business Blog are those of the author alone and do not represent those of British Gas. The accuracy, completeness and validity of any statements made within this blog are not guaranteed. British Gas accepts no liability for any errors, omissions or representations. The copyright in the content within the British Gas Business Blog belongs to the authors of such content and any liability with regards to infringement of intellectual property rights remains with them. See the Fuel mix used to generate our electricity. Read about making a complaint about your business energy.